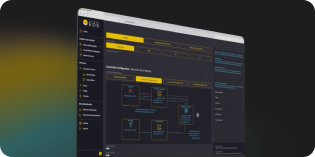
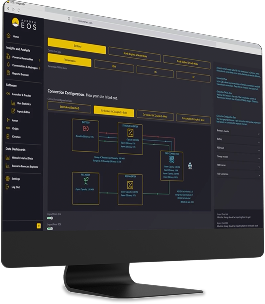
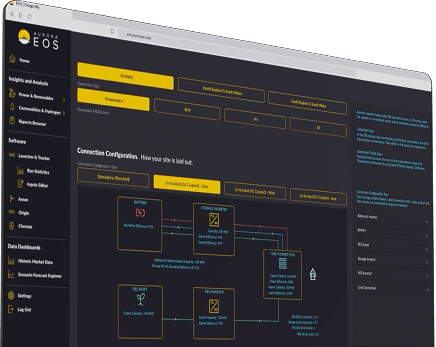
We provide decision-makers with actionable intelligence
to navigate and capitalise on the global shift in energy systems.

Clients
+
Countries
+
Transactions
+
Advisory Projects
Strategic market focus
for your sector
Financial Sector
For informed capital allocation in evolving energy landscapes, energy investors trust Aurora's analytical rigour and regulatory expertise.
Energy Consumers
Large-scale businesses optimising energy procurement, balancing cost-efficiency, reliability, and sustainability while meeting operational and regulatory requirements.
Utilities
Organisations managing energy generation, transmission, and distribution, optimising grid performance and integrating renewables to meet future energy demand.
All voices, all markets
Article
The Limits To Growth: The Malaysian Way of Navigating the Data Centre Boom



Public Webinar
Curtailment in Spain: How exposed will your assets be?



Market Report
Western Regionalization: Day-Ahead Market Benefits Analysis for Arizona Balancing Authorities